


Next: Kinematic variables
Up: Basic Formula
Previous: Extracting physics asymmetry from
The statistical error of the asymmetries are:
The statistical error of  and
and 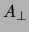 can be obtained from:
can be obtained from:
where 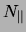 (
(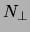 ) is the number of scattered electrons when
the beam polarization is parallel or antiparallel (perpendicular) to the
target polarization.
) is the number of scattered electrons when
the beam polarization is parallel or antiparallel (perpendicular) to the
target polarization.
The error of  for each kinematics can be written as:
for each kinematics can be written as:
To minimize 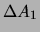 we need
we need
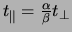 .
.
Xiaochao Zheng
2002-05-09
![$\displaystyle \big({\frac{1}{P_tP_bf}}\big)^2
\big[{\big({\frac{1}{D(1+\eta\xi)...
...a A_{\parallel}}\big)^2
+\big({\frac{\eta}{d(1+\eta\xi)}A_{\perp}}\big)^2}\big]$](img56.png)
![$\displaystyle \big({\frac{1}{P_tP_bf}}\big)^2
\big[{\big({\frac{1}{D(1+\eta\xi)...
...a A_{\parallel}}\big)^2
+\big({\frac{\eta}{d(1+\eta\xi)}A_{\perp}}\big)^2}\big]$](img56.png)
![]() and
and ![]() can be obtained from:
can be obtained from:
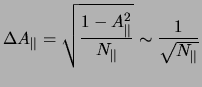
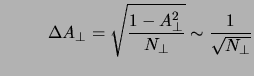
![]() for each kinematics can be written as:
for each kinematics can be written as:
![]() we need
we need
![]() .
.