



Next: Flammable Gas Detectors
Up: Flammable Gas
Previous: Flammable Gas
Contents
Hall A contains a lot of electrical equipment and almost all of it
could serve as an ignition source in the presence of an explosive
oxygen and hydrogen mixture. We have made an effort to minimize the dangers
from the equipment that is most likely to come into contact with
hydrogen gas.
There are a number of electrically powered devices associated with the
target gas handling system.
All the pressure transducers in the system are approved
for use in a hydrogen atmosphere.
The solenoid valves on the gas panels are explosion-proof.
The AC power for the solenoids is
carried by wires which are contained in either hard or flexible conduit.
There are also LEDs on the gas panels that provide an indication as to the
status of the valve solenoids. These are powered by a 24  DC supply.
The readouts for the pressure transducers are
mounted on the gas panels and the AC power for these readout units
is in conduit. All the pressure transducers have 4-20 mA outputs.
DC supply.
The readouts for the pressure transducers are
mounted on the gas panels and the AC power for these readout units
is in conduit. All the pressure transducers have 4-20 mA outputs.
In addition to the electrical devices in the gas handling system,
there are a number of devices inside of or mounted on the scattering
chamber.
All the devices which are in the scattering chamber must have
their power delivered to them by wires in vacuum. The
insulation of these wires should be radiation resistant, so Kapton
has been used where available.
The following electrical items are in close proximity to
or are actually in the hydrogen system.
- Axial Circulation Fan
- The fans which
circulate the hydrogen in the target are AC induction motors
and therefore contain no brushes and are practically immune to sparking.
The three phase power for these fans is delivered to them by 18
gauge stranded copper wire with Kapton insulation.
The maximum current that
the fans draw is 5
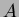 for a maximum power consumption of
200
for a maximum power consumption of
200 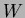 when pumping liquid hydrogen/deuterium. The current and voltage drawn
by the fans is monitored by the control system.
when pumping liquid hydrogen/deuterium. The current and voltage drawn
by the fans is monitored by the control system.
- Fan Motor Tachometer
- The fans have a tachometer which consist of a
coil that views the flux change caused by a permanent magnet attached to
the motor rotor. The tachometer signals are carried on 22 gauge stranded wire
with Kapton insulation. This is a low power signal. The control system
monitors the frequency of the fans.
- Low Power Heater
- This is a ``hair dryer'' style heater ( it
resembles the heater elements found in hair dryers and heat guns) that
is immersed in the hydrogen. The heater is made of 0.0179
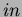 diameter
Nichrome wire with a resistance of 1.993
diameter
Nichrome wire with a resistance of 1.993 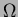 per foot wrapped
on a G10 carrier board.
The maximum power available to this
heater is 80
per foot wrapped
on a G10 carrier board.
The maximum power available to this
heater is 80 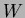 . The power for the low power heater is supplied by
a Oxford ITC-502 temperature controller. The heater lead wire is
18 gauge Kapton insulated copper stranded wire. The heaters have a
DC resistance of 20
. The power for the low power heater is supplied by
a Oxford ITC-502 temperature controller. The heater lead wire is
18 gauge Kapton insulated copper stranded wire. The heaters have a
DC resistance of 20 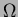 and hence will draw a maximum of 2
and hence will draw a maximum of 2 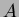 .
The power supplied to this heater is monitored by the control system.
.
The power supplied to this heater is monitored by the control system.
- High Power Heater
- There are two kapton enclosed incoloy heater foils
wrapped on the inside wall of each heat exchanger.
The maximum power available to each
heater is 500
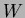 . The heater has a DC resistance of
26
. The heater has a DC resistance of
26 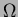 and two heaters in parallel
are driven by a 150
and two heaters in parallel
are driven by a 150  , 7
, 7 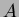 power supply.
The current and voltage supplied to this heater are monitored by the control
system and there
is a software power maximum enforced on the power setting
of this heater.
The heater is connected to
the outside world by 18 gauge stranded wire with Kapton insulation.
power supply.
The current and voltage supplied to this heater are monitored by the control
system and there
is a software power maximum enforced on the power setting
of this heater.
The heater is connected to
the outside world by 18 gauge stranded wire with Kapton insulation.
- Resistors
- There are two Allen Bradley and four Cernox
resistors immersed in each target loop. These resistors provide temperature
measurements of the target fluid. The temperature controllers that
read them use a current of less than 30
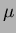 A to excite them (
they are excited with a constant voltage which for our resistors is
on the order of 30 mV). The Cernox resistors are connected to the outside world
with quad strand 36 gauge phosphor bronze wire with Formvar insulation.
The Allen Bradley resistors are wired with 30 gauge Kapton insulated
copper stranded wire.
A to excite them (
they are excited with a constant voltage which for our resistors is
on the order of 30 mV). The Cernox resistors are connected to the outside world
with quad strand 36 gauge phosphor bronze wire with Formvar insulation.
The Allen Bradley resistors are wired with 30 gauge Kapton insulated
copper stranded wire.
- Target Lifter
- There are two AC servo motors which provide
the power to lift the target ladder. These motors are powered by three
phase 208
 power and are equipped with fail safe brakes (the brakes are
released by a 24
power and are equipped with fail safe brakes (the brakes are
released by a 24  DC control voltage)
and 50 to 1 gear reducers. On power up, there is a delay relay
that insures that
the motors are always energized before the brakes are released.
DC control voltage)
and 50 to 1 gear reducers. On power up, there is a delay relay
that insures that
the motors are always energized before the brakes are released.
- Vacuum Pumps
- The scattering chamber is evacuated by two Leybold
1000
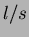 turbo pumps that are backed by a Leybold 65
turbo pumps that are backed by a Leybold 65 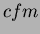 mechanical pump. The turbo pumps are powered by 120
mechanical pump. The turbo pumps are powered by 120  AC power while the
backing pump requires three phase 208
AC power while the
backing pump requires three phase 208  AC power. The motor on the backing
pump is explosion proof and approved for use in NEC Class 1, Division 1,
Group D (hydrocarbons but not hydrogen) environments. An identical
mechanical pump is used in the pump and purge system of the gas panels.
Both the scattering chamber backing pump and the
pump and purge system's mechanical pump exhaust to the vent line.
AC power. The motor on the backing
pump is explosion proof and approved for use in NEC Class 1, Division 1,
Group D (hydrocarbons but not hydrogen) environments. An identical
mechanical pump is used in the pump and purge system of the gas panels.
Both the scattering chamber backing pump and the
pump and purge system's mechanical pump exhaust to the vent line.
- Vacuum Gauges
- The chamber vacuum is monitored by an
HP cold cathode gauge. This gauge has a maximum operating voltage of
4000
 and a maximum
current of 133
and a maximum
current of 133 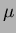 A. The pressure at the entrance to the roughing pump
is measured by a convectron gauge.
A. The pressure at the entrance to the roughing pump
is measured by a convectron gauge.




Next: Flammable Gas Detectors
Up: Flammable Gas
Previous: Flammable Gas
Contents
Joe Mitchell
2000-02-29
![]() DC supply.
The readouts for the pressure transducers are
mounted on the gas panels and the AC power for these readout units
is in conduit. All the pressure transducers have 4-20 mA outputs.
DC supply.
The readouts for the pressure transducers are
mounted on the gas panels and the AC power for these readout units
is in conduit. All the pressure transducers have 4-20 mA outputs.