



Next: Control System
Up: General Description
Previous: Physics Principle
Contents
High power diode lasers (about 100W) provide an intense monochromatic
light beam for optical pumping. The lasers are housed in a large
shielding house, known as the ``laser hut'', which is located about 5m
away from the target on one side of the beam line. An overview of a
typical arrangement of the target components in the Hall is shown in
Figure ![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) .
.
Figure:
Overview of the target setup. Shown are the laser hut, the
beam pipes covering the laser beam line extending to the target area,
and the Helmholtz coils with the RF assembly and support sub-assembly.
|
|
The polarized target comprises several
components beyond its target cell (see Fig. ![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) )
related to its operation, they are in section:
)
related to its operation, they are in section:
- A double sets of Helmholtz coils which provide the target spins with a
holding magnetic field
of few tens of Gauss as well as define the orientation of the
polarization in any required
direction.
- A pair of RF coils which allow for the measurement of the target
polarization
using the Adiabatic Fast Passage (AFP) technique and the Electron
Paramagnetic
Resonance (EPR) technique.
- A multi-purpose RF enclosure which holds the RF coils but more
importantly is crucial for the
containment of the target cell in case of explosion. It also provides a
containment volume for the
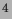 He gas to cool the target windows with cooling jets, minimizing the
radiation length crossed by the electron beam.
He gas to cool the target windows with cooling jets, minimizing the
radiation length crossed by the electron beam.
- An oven with all its related components for providing the necessary
temperature to the pumping cell in order to bring the rubidium in its
vapor phase
and control its number density.
- A target ladder subassembly which supports a target cell, a reference
cell, (which can be filled with
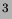 He, Nitrogen or
He, Nitrogen or 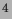 He gas with pressure
up to 10 atmospheres to study dilution, density or background),
a 7-foil
He gas with pressure
up to 10 atmospheres to study dilution, density or background),
a 7-foil  C optics target, a
BeO beam viewer and an oven. It also includes a full mechanism
for positioning the targets
and bears the target cell viewing mirrors and the optical beam line
mirrors.
C optics target, a
BeO beam viewer and an oven. It also includes a full mechanism
for positioning the targets
and bears the target cell viewing mirrors and the optical beam line
mirrors.
- A laser shielding house known as ``laser hut'' where two laser beam lines
are formed by seven 30-Watt diode lasers.
These laser beam lines are used for optical
pumping of the rubidium alkali atoms in the direction either along the
electron beam (longitudinal, 4 lasers) or perpendicular to the electron
beam line (transverse, 3 lasers). The nominally longitudinal laser beam
can also be directed at a different (specific) direction.




Next: Control System
Up: General Description
Previous: Physics Principle
Contents
Xiaochao Zheng
2001-06-01
![]() .
.
![\includegraphics[scale=0.6]{overview_may23.eps}](img3.png)
![]() )
related to its operation, they are in section:
)
related to its operation, they are in section: